Restriction enzymes cut DNA strands at points on restriction sites. APPLICATION OF RESTRICTION ENZYMES They are used in gene cloning and protein expression experiments.

What S New Cloning Infographic Thermo Scientific Teaching Biology Study Biology Science Biology
Lipases This enzyme would help the process of digestion by disintegrating fatty food.

. Type I Type II and Type III. Type I restriction enzymes are also called restriction endonucleases. For this reason they are indispensible tools of recombinant DNA technology genetic engineering.
517 describe the process of micropropagation tissue culture in which small pieces of plants explants are grown in vitro using nutrient media. These restriction enzymes recognize certain sequences of DNA and cleave them at a site. Each restriction endonuclease functions by inspecting the length of a DNA sequence.
Restriction enzymes are used for many different purposes in biotechnology. 518 understand how micropropagation can be used to produce commercial quantities of identical plants clones with desirable characteristics. A restriction enzyme makes a cut in each of the two strands of DNA creating a free 3-OH group and a free 5-phosphate group.
The sugar present in milk is lactose and by the help of lactase it is disintegrated into galactose and glucose. The former group is useful for making recombinant DNA. There are three types of Restriction Enzymes.
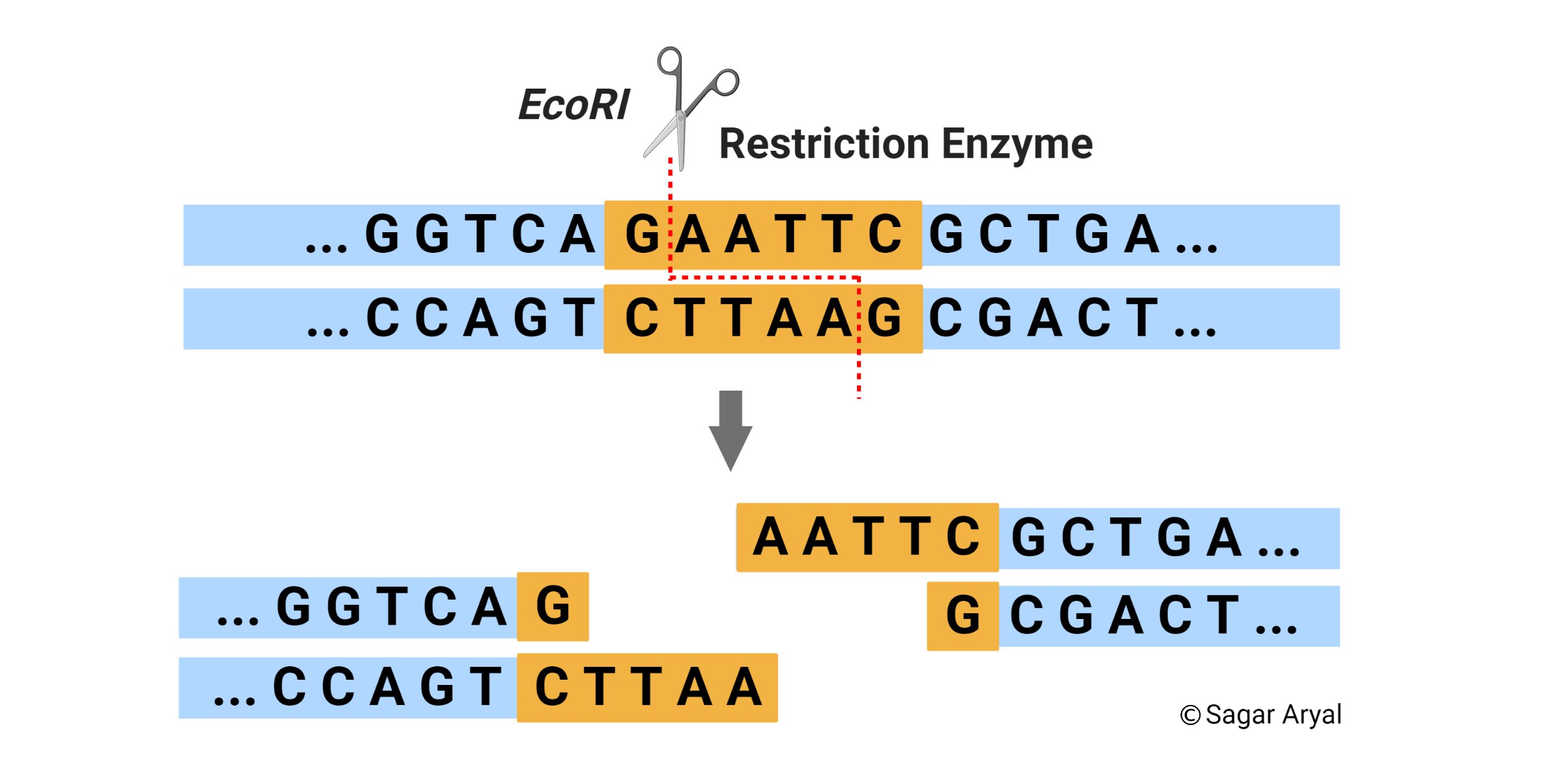
You can think of restriction enzymes as molecular scissors. Restriction enzymes can be isolated from bacterial cells and used in the laboratory to manipulate fragments of DNA such as those that contain genes. An extremely important use of.
Restriction enzymes are also frequently used to verify the identity of a specific DNA fragment based on the known restriction enzyme sites sequence that it contains. A restriction enzyme is a DNA-cutting enzyme that recognizes specific sites in DNA. Restriction enzymes are DNA-cutting enzymes found in bacteria and harvested from them for use.
Expert Answer A restriction enzyme is a bacteria-produced protein that can cleave DNA at its corresponding restrictionsite. A restriction enzyme is an enzyme that cuts DNA after recognizing a specific sequence of DNA. Briefly describe the characteristics and the applications of a restriction enzyme.
Lactase The enzyme is secreted in the small intestine of the human body while the process of digestion is going on. Restriction enzymes can be used to map DNA fragments or the entire genome thus determining the specific order of the restriction enzyme sites in the genome. Majority of restriction enzymes cuts DNA strands within the restriction site while some makes cuts outside it.
4 The enzyme recognizes a specific palindromic nucleotide sequence in the. A restriction enzyme is a kind of nuclease enzyme which is capable of cleaving double-stranded DNA. 1 The enzyme cuts DNA molecule at identified position within the DNA.
Once it finds its specific recognition sequence it will bind to the DNA and cut each of the two strands of the double helix at specific points in their sugar-phosphate backbone. A restriction enzyme recognizes and cuts DNA only at a particular sequence of nucleotides. The nucleotide sequence at a restriction site is recognized by the restriction enzyme and.
Many restriction enzymes make staggered cuts at or near their recognition sites producing ends with a single-stranded overhang. 3 The enzyme cuts the sugar-phosphate backbone at specific sites on each strand. The enzyme binds DNA at specific sites and cuts only one of the two strands Restriction enzymes cut DNA molecules at a particular point by recognising a specific sequence.
Because they cut within the molecule they are often called restriction endonucleases. This pattern of DNA fragments generates a DNA fingerprint and each. Each restriction endonuclease functions by inspecting the length of a DNA sequence.
Because of the sequence specificity of restriction enzymes these enzymes can cut DNA into discrete fragments which can be resolved by gel electrophoresis. Such enzymes can be used to splice and insert segments of DNA into other segments of DNA thereby providing a means to modify DNA and construct new forms. Restriction enzymes cut DNA molecules at a particular point by recognising a specific sequence.
Used in recombinant DNA technology since they cut the DNA in a staggered manner creating sticky ends that bond with complementary sticky ends of other fragments. Restriction enzymes cut the strand of DNA a little away from the centre of the palindrome sites but between the same two bases on the opposite strands. Each restriction endonuclease recognises a specific palindromic nucleotide sequence sequence of base pairs that reads same on the two strands when the orientation of reading is kept the same in the DNA.
The recognition sites are palindromic in origin that is they are the sequences which are read the same forward and backward. The enzymes may cleave DNA at random or specific sequences which are referred to as restriction sites. If two DNA molecules have matching ends they can be joined by the enzyme DNA ligase.
Restriction enzymes are used in biotechnology to cut DNA into smaller strands in order to study fragment length differences among individuals Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism RFLP. 1-Describe the natural function of restriction enzymes and explain how they are used in recombinant DNA technology. Restriction endonucleases also called as molecular scissors are a class of nuclease enzymes which cut the DNA strand at precise locations.
View the full answer Transcribed image text. 2 The enzyme binds DNA at specific sites and cuts only one of the two strands. Restriction enzymes Restriction endonuclease such as reverse transcriptase cut gene from genome which leaves sticky ends with the same restriction enzyme it also cuts the plasmid or artificial chromosome.
Type II restriction enzymes are made up of four. In the bacterial cell restriction enzymes cleave foreign DNA thus eliminating infecting organisms. Scientists can use restriction enzymes to.
The complementary sticky ends join and form hydrogen bond together and DNA ligase seals the sugar phosphate backbone to form a recombinant DNA. A common use for restriction enzymes is to generate a fingerprint of a particular DNA molecule. They are made of two long strands of DNA joined together.

Biotechnology Reading And Guided Notes In 2021 Biotechnology Guided Notes Learning Targets
0 Comments